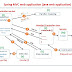
A thread goes through
various stages while executing or completing task like new/born, ready,
runnable and finally dead state, these states are nothing but is life cycle of a
Thread.
Below is the diagram
which tells the story of Thread life cycle i.e. how a thread goes into ready state from born state and from ready to running and finally into Dead state. Please go through this to understand the life cycle of a Thread.
- When we write MyThread t1=new MyThread() then thread is in the New/Born state.
- When we call t.start() method then thread enters into Ready State or Runnable State.
- If Thread Scheduler allocates the processor to Thread then Thread enters into Running State.
- If run() method completes successfully then thread enters into Dead State.
above are the basic main states of the Thread. but apart from this it has some condition through that it goes into different states like waiting state,suspended state,sleeping state.the full description is below.
1. If a running thread calls the Thread.yield() method then thread enters into ready state from running state to give chance to other waiting thread of same priority immediately.
1. If a running thread calls the Thread.yield() method then thread enters into ready state from running state to give chance to other waiting thread of same priority immediately.
2. If a Thread calls the join() method then it enters into waiting state and if this thread comes out from waiting state/blocked state then it enters into Ready/Runnable state but here is some condition to come out from the waiting state is-
A) If thread completes its own execution.
B) If time expires.
C) If waiting thread got interrupted.
3. If running thread calls the sleep() then immediately enters into sleeping state. now thread will come out of this state to ready state only when-
A) If time expires.
B) If sleeping thread got interrupted.
4. If thread calls the wait() method then running thread will enters into waiting state. if this thread got any notification by method notify()/notifyAll() then it enters into another waiting state to get lock.so when the thread comes out of waiting state to another waiting state to get lock is-
A) If waiting thread got notification.
B) If time expires.
C) If waiting thread got interrupted.
Now thread which is in the another waiting state will go to ready state when it get the lock.
5. If running thread calls the suspend() method now thread enters into suspended state and it will comes out form there to ready state only when it will call the resume() method.
6. If running thread calls the stop() method then immediately enters into dead state.
Note: now the methods suspend(), resume(),stop() are deprecated and not recommended to use.
So,this is the whole life cycle of the thread by which it goes through.