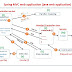
Multithreading is a process of creating multiple threads in java stack area (JSA) for executing multiple task concurrently to complete their execution
in less time by using processor ideal time effectively.
Output
now what is process? if we talk about
process we can say that program under execution is called process. and lightweight
process is called thread . in other way we can say ,Thread is
independent sequential flow of execution.
Multithreading is also lightweight because
of the contexts switching is very fast
and effective among threads.and switching is very fast because of thread stored
in same address.
When JVM is created in its JSA area by default
two threads are created these are following….
- Main thread-to execute java methods
- Garbage collector-to destroy unreferenced objects
We can create thread by 4 ways, these are
following
- By extending Thread class
- By implementing Runnable interface
- By implementing Callable interface
- By anonymous class (Inline Thread)
By extending Thread class
class ThreadUsingThread extends Thread
{
public void
run()
{
System.out.println("I am form run");
}
public static void
main(String[] args)
{
ThreadUsingThread t = new
ThreadUsingThread();
t.start();
}
}
We can define a Thread even by implementing Runnable
interface also.Runnable interface present in java.lang.pkg and contains only
one method run().
class ThreadUsingRunnable implements
Runnable
{
public void
run()
{
System.out.println("I am form run");
}
public static void
main(String[] args)
{
ThreadUsingThread tut = new
ThreadUsingThread();
Thread t=new
Thread(tut);
t.start();
}
}
By implementing Callable interface
- In the Case of Runnable Job Thread won’t Return anything.
- If a Thread is required to Return Some Result after Execution then we should go for Callable.
- Callable Interface contains Only One Method public Object call() throws Exception.
- If we Submit a Callable Object to Executor then the Framework Returns an Object of Type java.util.concurrent.Future
- The Future Object can be Used to Retrieve the Result from Callable Job.
import
java.util.concurrent.*;
class
ThreadUsingCallable implements Callable
{
int num=10;
public
Object call() throws Exception
{
return num;
}
public static void
main(String[] args) throws Exception
{
ThreadUsingCallable
tuc = new ThreadUsingCallable();
ExecutorService
service=Executors.newFixedThreadPool(3);
Future
f=service.submit(tuc);
System.out.println(f.get());
service.shutdown();
}
}
Output
By anonymous class (Inline Thread)
Actually there are two way to create inline Thread,these are-
- Create anonymous class with Thread object
- Create anonymous class with Runnable object
class
ThreadUsingAnonymous
{
public static void
main(String[] args)
{
Thread thread
= new Thread() {
@Override
public void
run() {
System.out.println("Hello World!");
}
};
thread.start();
}
}
Above is created by using Thread object.we can class start() method just between the "};" by "}.start();" .
Using Runnable object
class
ThreadUsingAnonymous
{
public static void
main(String[] args)
{
Thread thread
= new Thread(new Runnable() {
@Override
public void
run() {
System.out.println("Hello World!");
}
});
thread.start();
}
}
Above is created by using Thread object.we can class start() method just between the ");" by ").start();" .