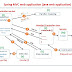
Serialization:
It is a process of converting object into stream
of bytes (byte []) and storing that object data in a file permanently or
sending it through network to use this object data in remote computer is called
Serialization.
In other words we can say that the process of writing
or saving the value/state of an object from java supported form to either
network supported form or to a file supported form is known as Serialization.
De-Serialization:
It is process of reading
stream of bytes object data from the file and storing it in JVM object memory
is called De-Serialization.
In other words we can say that the process of
reading the value/state of an object from file is called De-Serialization.
Click above diagram to enlarge.
Important API to perform the Serialization and
De-Serialization
- By using FileOutputStream and ObjectOutputStream classes we can perform the operation of Serialization.
- By using FileInputStream and ObjectInputStream classes we can perform the operation of De-Serialization.
For
Serialization:
following are the steps to perform the Serialization:
following are the steps to perform the Serialization:
1-Create FileOutputStream
object and pass the file name as parameter.
FileOutputStream fos=new FileOutputStream("abc.txt");
2-Create ObjectOutputStream
object and pass the object of FileOutputStream object as parameter.
ObjectOutputStream
oos=new
ObjectOutputStream(fos);
3-Call writeObject() method by ObjectOutputStream object and
pass the object in writeObject(ObjectTobeSerialize) method that is to be
Serialize.
oos.writeObject(ObjectToBeSerialize);
4-Serialization process completed object saved into given file.
For De-Serialization:
following are the steps to perform the De-Serialization:
1-Create FileInputStream object and pass the file name as parameter.
FileInputStream fis=new FileInputStream("abc.txt");
2-Create ObjectInputStream object and pass the object of FileInputStream object as parameter.
ObjectInputStream ois=new ObjectInputStream(fis);
3-Call readObject() method by ObjectInputStream object.
Object obj=ois.readObject();
4-De-Serialization process completed and object retrieved from file.
Concept of serialVersionUID :
serialVersionUID is used to ensure that same class(That was used during Serialization) is loaded during Deserialization.serialVersionUID is used for version control of object.You can read more at serialVersionUID in java serialization.
private static final long serialVersionUID =
1L;
- It is a private static final long datatype variable.
- It is used for identifying class changes.
- It is automatically created by compiler at the time of compilation.
- The no. is generated based on the code we placed in class.
- If modification is done and we compile the class then it will generate the new serialVersionUID .
Example:
Below is the example which shows that how Serialization and Deserialization is performed.
//BankAccount.java
import
java.io.*;
class
BankAccount implements Serializable {
public int accNo;
public
String accName;
public int balance;
private static final long serialVersionUID = 1L;
}
//SerializationDemo.java
import
java.io.*;
class
SerializationDemo {
public static void
main(String[] args) {
// Serialization
try
{
// Saving of object in a file
FileOutputStream file
= new FileOutputStream("Bank.ser");
ObjectOutputStream out
= new ObjectOutputStream(file);
BankAccount acc1
= new BankAccount();
acc1.accNo
= 34043;
acc1.accName
= "CH";
acc1.balance
= 5000;
// Method for serialization of object
out.writeObject(acc1);
out.close();
file.close();
System.out.println("Object has been serialized");
} catch
(IOException ex) {
System.out.println("IOException is caught");
}
}
}
Output
Object has been serialized
//DeSerializationDemo.java
import
java.io.*;
class
DeSerializationDemo {
public static void
main(String[] args) {
// Deserialization
try
{
// Reading the object from a file
FileInputStream file
= new FileInputStream("bank.ser");
ObjectInputStream in
= new ObjectInputStream(file);
// Method for deserialization of object
Object obj
= in.readObject();
BankAccount acc1
= (BankAccount) obj;
in.close();
file.close();
System.out.println("Object has been deserialized ");
System.out.println("accNo= " + acc1.accNo);
System.out.println("accName = " + acc1.accName);
System.out.println("balance = " + acc1.balance);
}
catch
(IOException ex) {
System.out.println("IOException is caught");
}
catch
(ClassNotFoundException ex) {
System.out.println("ClassNotFoundException is caught");
}
}
}
Output:
Object has been deserialized
accNo= 34043
accName = CH
balance = 5000