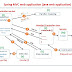
Method overloading deals with the notion of having two or more methods in the same class or from parent class with the same name but different arguments.
void foo(int a)
void foo(int a, float b)
Method overriding means having two methods with the same arguments, but different implementations. One of them would exist in the parent class, while another will be in the derived, or child class. The
@Override annotation, while not required, can be helpful to enforce proper overriding of a method at compile time.class Parent {
void foo(double d) {
// do something
}
}
class Child extends Parent {
@Override
void foo(double d){
// this method is overridden.
}
}
Property
|
Overloading
|
Overriding
|
Method
names
|
Must
be same.
|
Must
be same.
|
Argument
type
|
Must be different(at
least order)
|
Must be same including order.
|
Method
signature
|
Must
be different.
|
Must
be same.
|
Return
types
|
No restrictions.
|
Must be same until 1.4v but from 1.5v
onwards we can take co-variant return types also.
|
private,
static, final methods
|
Can
be overloaded.
|
Can
not be overridden.
|
Access
modifiers
|
No restrictions.
|
Weakening/reducing is not allowed.
|
Throws
Clause
|
No
restrictions.
|
If
child class method throws any checked exception compulsory parent class
method should throw the same checked exceptions or its parent but no
restrictions for un-checked exceptions.
|
Method
Resolution
|
Is always takes care by compiler
based on referenced type.
|
Is always takes care by JVM based on
runtime object.
|
Also
known as
|
Compile
time polymorphism (or)
static(or)early
binding.
|
Runtime
polymorphism (or) dynamic (or) late binding.
|